Low FODMAPS / IBS Diet
What Is A Low FODMAPS / IBS Diet?
FODMAPs are Fermentable, Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides and Polyols (sugar alcohols) that are poorly absorbed in the small intestine. They are osmotic, meaning they pull water into the intestinal tract. When consumed in excess, they may be fermented by intestinal bacteria, which can lead to gas, bloating, cramping and/or diarrhea and other symptoms common with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Eliminating dietary FODMAPs might alleviate these symptoms. In addition to what is listed below, raw, unsalted nuts and seeds (except for pistachios) are allowed in appropriate serving sizes (2 Tablespoons). You’ll have many foods you can eat on this diet, but there’s a steep learning curve about which foods are high in FODMAPs and what you could choose instead.
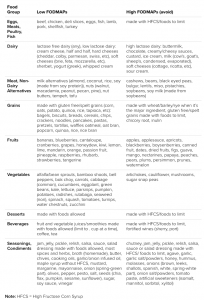
Foods High In FODMAPs
- Anything made with wheat, barley, or rye
- Apples
- Artichokes
- Artificial sweeteners like in chewing gum
- Beans
- Cashews
- Cauliflower
- Dried fruits
- Garlic and onions
- High-fructose corn syrup
- Honey
- Ice cream
- Mushrooms
- Pistachios
- Watermelon
Foods Low In FODMAPs
- Almond, coconut, rice, and soy milk
- Bananas
- Bell peppers
- Blueberries
- Carrots
- Cucumbers
- Grapes
- Oats
- Potatoes
- Quinoa
- Rice
- Spinach, kale, and other leafy greens
- Tangerines
- Tomatoes
Follow the low-FODMAP diet for 6 weeks. After this, if symptoms have resolved, you can add foods back in one at a time to identify your trigger foods. Please schedule an appointment with our dietitian to oversee this “challenge phase”.


